Introduction
When evaluating the success or value of an investment, project, or policy, the concept of net benefits plays a crucial role. But what exactly are net benefits, and why are they so important? Understanding net benefits helps individuals, businesses, and governments make informed decisions that maximize positive outcomes and minimize costs. In this article, we’ll explore the definition of net benefits, how they are measured, and their significance in various contexts.
Defining Net Benefits
Economic Net Benefits
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This process involves comparing the total costs of a project or investment with its total benefits. Net benefits are calculated by subtracting the costs from the benefits, giving a clear picture of whether the investment is worthwhile.
- ROI (Return on Investment): ROI measures the profitability of an investment. It’s calculated by dividing the net benefits by the costs. A higher ROI indicates a more beneficial investment.
Social Net Benefits
- Community Impact: Social net benefits refer to the positive effects on communities, such as improved infrastructure, education, or healthcare. These benefits enhance the quality of life and contribute to societal well-being.
- Quality of Life Improvements: Evaluating social net benefits involves assessing how projects or policies improve living conditions, health, and overall satisfaction.
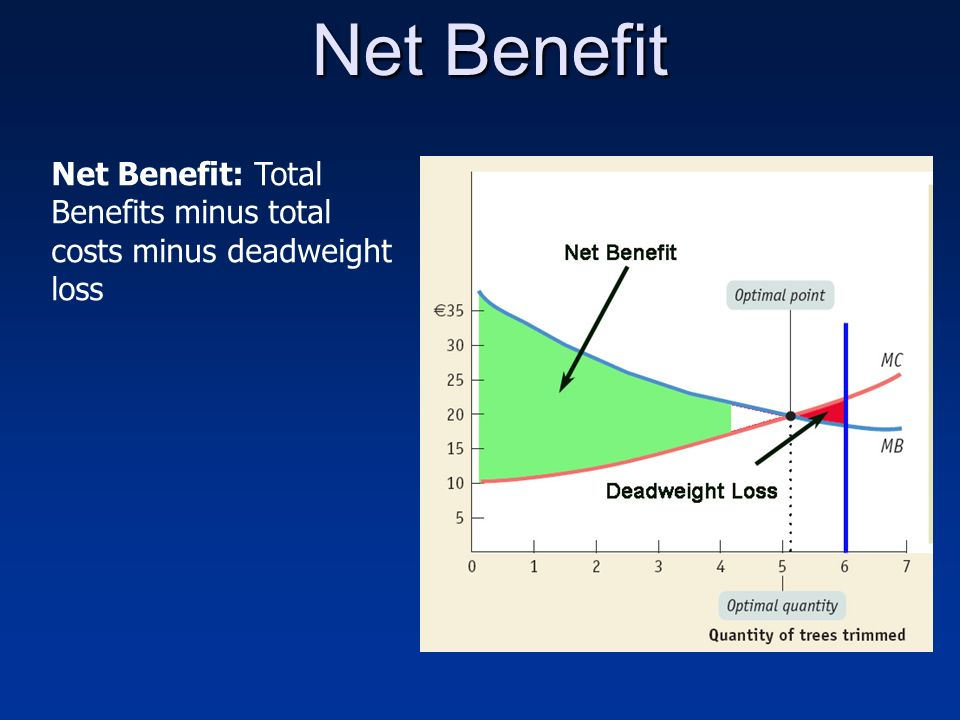
Measuring Net Benefits
Quantitative Measures
- Financial Metrics: These include direct financial benefits such as increased revenue, cost savings, or profit margins. Quantitative measures are essential for evaluating economic net benefits.
- Performance Indicators: Metrics like productivity, efficiency, and output are used to measure how well an investment or project performs in achieving its goals.
Qualitative Measures
- Surveys and Feedback: Gathering feedback from stakeholders, customers, or community members provides insights into the intangible benefits that might not be captured through financial metrics alone.
- Case Studies: Analyzing specific examples of projects or investments helps illustrate the broader impacts and benefits that might be difficult to quantify.
Net Benefits in Business
Investment Decisions
- Evaluating Projects: Businesses use net benefits to assess the potential value of new projects or ventures. This helps in making strategic decisions about where to allocate resources.
- Strategic Planning: Understanding net benefits aids in long-term planning, helping businesses prioritize projects that offer the highest returns.
Marketing and Sales
- Customer Value Proposition: Companies analyze net benefits to determine how their products or services provide value to customers, which can enhance their marketing strategies.
- Competitive Advantage: By focusing on the net benefits of their offerings, businesses can differentiate themselves from competitors and attract more customers.
Net Benefits in Public Policy
Policy Evaluation
- Government Projects: Public sector projects are evaluated based on their net benefits to ensure that taxpayer money is used effectively. This includes infrastructure, social services, and more.
- Social Programs: Evaluating the impact of social programs involves assessing the improvements in public health, education, and community well-being.
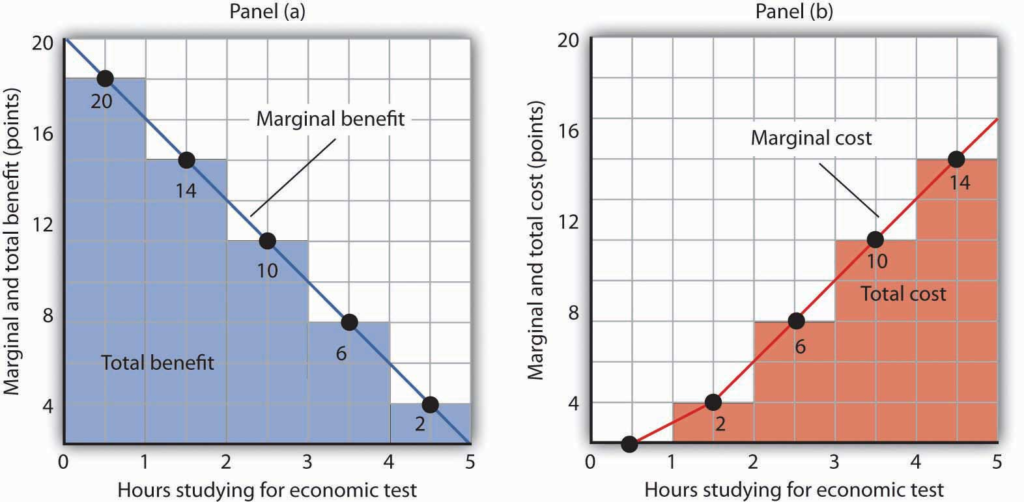
Impact Assessment
- Environmental Policies: Net benefits are used to measure the effectiveness of policies aimed at environmental conservation and sustainability.
- Health Initiatives: Public health programs are evaluated based on their net benefits in reducing disease, improving health outcomes, and enhancing quality of life.
Challenges in Calculating Net Benefits
Data Limitations
- Incomplete or Inaccurate Data: Accurate measurement of net benefits requires reliable data. Incomplete or erroneous data can lead to misleading conclusions.
- Measurement Errors: Errors in data collection or analysis can affect the accuracy of net benefit calculations.
Subjectivity
- Bias in Benefit Assessment: Personal or organizational biases can influence how benefits are assessed, potentially skewing results.
- Difficulty in Valuing Intangible Benefits: Some benefits, such as improved quality of life or community cohesion, are challenging to quantify and may be underestimated.
Strategies for Maximizing Net Benefits
Optimizing Resource Allocation
- Efficient Use of Funds: Allocating resources effectively ensures that investments yield the highest possible net benefits.
- Prioritizing High-Impact Areas: Focusing on projects or areas with the greatest potential for positive outcomes helps maximize overall benefits.
Stakeholder Engagement
- Involving Community Input: Engaging with stakeholders and community members provides valuable insights and ensures that projects meet their needs and preferences.
- Addressing Diverse Needs: Considering the diverse needs of different groups helps in designing initiatives that offer broad net benefits.
Examples of Net Benefits in Practice
Corporate Sector
- Successful Business Ventures: Companies that have effectively analyzed and leveraged net benefits often achieve higher profitability and competitive advantage.
- Innovations with High Returns: Innovations that provide significant net benefits, such as new technologies or processes, drive business growth and success.

Public Sector
- Effective Social Programs: Programs that improve public health, education, and social services demonstrate substantial net benefits to society.
- Community Development Projects: Projects aimed at community development, such as building parks or improving transportation, provide significant net benefits to local populations.
Future Trends in Net Benefits Analysis
Technological Advances
- Data Analytics and AI: Advances in data analytics and artificial intelligence enhance the ability to measure and predict net benefits more accurately.
- Enhanced Measurement Tools: New tools and methodologies improve the precision of net benefit calculations, incorporating both quantitative and qualitative data.
Evolving Criteria
- Shifts in Priorities: Changing societal and organizational priorities influence how net benefits are evaluated and what criteria are considered.
- New Evaluation Metrics: Emerging metrics and frameworks provide more comprehensive assessments of net benefits, addressing evolving needs and contexts.
Conclusion
Understanding and analyzing net benefits is crucial for making informed decisions in both business and public policy. By evaluating the positive outcomes and comparing them with costs, individuals and organizations can ensure that their investments and initiatives yield the greatest possible value. Whether in the corporate sector or the public sphere, effective net benefits analysis leads to better decision-making and enhanced overall impact.
FAQs
- What are net benefits?
- Net benefits refer to the positive outcomes of a project or investment after subtracting the costs. They help determine the overall value or profitability.
- How are net benefits calculated?
- Net benefits are calculated by subtracting total costs from total benefits. Both quantitative and qualitative measures are used in the assessment.
- Why are net benefits important in business?
- Net benefits help businesses evaluate the value of investments and projects, guiding strategic decisions and enhancing profitability.
- What challenges are involved in measuring net benefits?
- Challenges include data limitations, measurement errors, and subjectivity in assessing intangible benefits.
- How can organizations maximize their net benefits?
- Organizations can maximize net benefits
Read More:
Digital Footprint
The Ultimate Guide to Make1M.com: Unlocking Your Path to Financial Freedom
The Ultimate Guide to Blue Shampoo: How It Works and Why You Need It
Understanding aiotechnical.com Health





