Introduction
In the fast-evolving world of healthcare, one concept stands out as a beacon of quality and reliability: Evidence-Based Practice (EBP). EBP is a systematic approach that integrates the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values to guide decision-making in healthcare. This approach ensures that patients receive care based on the most current and robust evidence available, ultimately improving outcomes and optimizing healthcare resources.
What is Evidence-Based Practice?
Definition of EBP
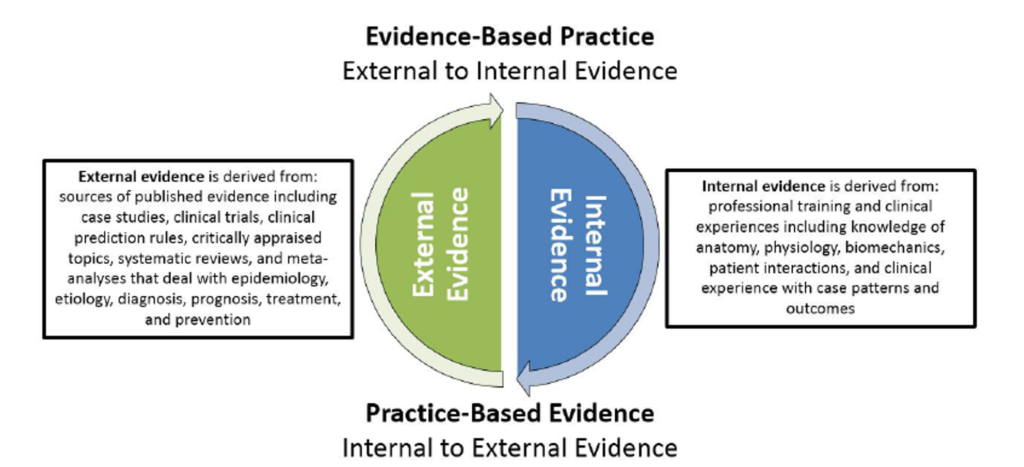
Evidence-Based Practice is defined as the conscientious use of current best evidence in making decisions about patient care. It involves the integration of clinical expertise, patient preferences, and the best research evidence into the decision-making process for patient care.
The Origins of EBP
The concept of EBP originated in the 1990s, stemming from the evidence-based medicine (EBM) movement. Initially focused on medical practice, it has since expanded to encompass various disciplines within healthcare, including nursing, psychology, and social work.
The Pillars of Evidence-Based Practice
1. Best Available Evidence
The foundation of EBP lies in the best available evidence, which typically comes from well-conducted research studies. These studies may include randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and meta-analyses that provide high-quality data on the effectiveness and safety of interventions.
2. Clinical Expertise
Clinical expertise refers to the skills and knowledge that healthcare providers acquire through their professional practice. It plays a crucial role in interpreting research evidence and applying it to the unique circumstances of each patient.
3. Patient Values and Preferences
Patient-centered care is a core aspect of EBP. It involves considering patients’ values, preferences, and individual circumstances when making healthcare decisions. This ensures that care is tailored to each patient’s needs and expectations.

The Process of Implementing Evidence-Based Practice
1. Formulating a Clinical Question
The first step in EBP is to develop a clear and focused clinical question. This question typically follows the PICO format: Patient/Problem, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome.
2. Searching for the Best Evidence
Once the clinical question is formulated, the next step is to search for the best available evidence. This involves conducting a thorough review of scientific literature using databases such as PubMed, Cochrane Library, and CINAHL.
3. Appraising the Evidence
After gathering evidence, it is essential to critically appraise its quality and relevance. This involves evaluating the study design, sample size, and potential biases to determine the strength of the evidence.
4. Applying the Evidence
The next step is to apply the evidence to clinical practice, considering the specific context of the patient. This may involve adapting guidelines or protocols based on the evidence to suit individual patient needs.
5. Evaluating the Outcomes
Finally, the impact of the applied evidence on patient outcomes is evaluated. This helps determine the effectiveness of the intervention and informs future clinical decisions.
The Importance of Evidence-Based Practice in Healthcare
Improving Patient Outcomes
EBP is vital for improving patient outcomes. By using interventions that have been proven effective through research, healthcare providers can reduce the risk of harm and enhance the quality of care.
Optimizing Healthcare Resources
EBP helps in the efficient use of healthcare resources by eliminating unnecessary or ineffective interventions. This is particularly important in a healthcare environment where resources are limited.
Enhancing Professional Development
Engaging in EBP encourages continuous professional development among healthcare providers. It fosters a culture of lifelong learning, critical thinking, and adaptability to new evidence.

Challenges in Implementing Evidence-Based Practice
Access to Quality Evidence
One of the main challenges in implementing EBP is access to high-quality evidence. Not all healthcare providers have access to comprehensive databases or the time to stay updated with the latest research.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is another significant barrier to EBP. Some healthcare professionals may be hesitant to adopt new practices or abandon long-standing methods, even in the face of new evidence.
Balancing Evidence with Clinical Expertise
While EBP emphasizes the use of the best available evidence, it also requires a balance with clinical expertise. Applying evidence without considering the nuances of individual patient cases can lead to suboptimal outcomes.
Overcoming Barriers to Evidence-Based Practice
Education and Training
Providing healthcare professionals with education and training in EBP is crucial for overcoming barriers. This includes teaching them how to search for, appraise, and apply evidence in their practice.
Institutional Support
Healthcare institutions play a critical role in supporting EBP by providing access to resources, such as databases and journals, and fostering a culture that encourages evidence-based decision-making.
Collaborative Practice
Collaborative practice among healthcare professionals can enhance the implementation of EBP. By working together, clinicians can share insights, discuss evidence, and develop best practices that benefit patients.
The Future of Evidence-Based Practice
Integration with Technology
As technology advances, the integration of EBP with electronic health records (EHRs) and decision support systems is likely to become more prevalent. This will enable real-time access to evidence and streamline the decision-making process.
Personalized Medicine
The future of EBP is closely linked with the rise of personalized medicine. By combining evidence with genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, healthcare providers can offer more tailored interventions.
Global Collaboration
Global collaboration in research and the sharing of evidence across borders will continue to strengthen EBP. This will help ensure that the best evidence is available to healthcare providers worldwide, regardless of location.
Conclusion
Evidence-Based Practice is the cornerstone of modern healthcare, ensuring that clinical decisions are grounded in the best available evidence. By integrating research, clinical expertise, and patient preferences, EBP enhances the quality of care, improves patient outcomes, and optimizes healthcare resources. Despite the challenges, the future of EBP is bright, with advancements in technology and global collaboration paving the way for more effective, personalized healthcare.
FAQs
1. What is the main goal of Evidence-Based Practice?
- The main goal of EBP is to improve patient outcomes by using the best available evidence to inform clinical decisions.
2. How does EBP benefit healthcare providers?
- EBP benefits healthcare providers by enhancing their decision-making process, encouraging continuous learning, and optimizing the use of resources.
3. Can Evidence-Based Practice be applied in all areas of healthcare?
- Yes, EBP can be applied across various healthcare disciplines, including medicine, nursing, psychology, and social work.
4. What are some common barriers to implementing EBP?
- Common barriers include access to quality evidence, resistance to change, and balancing evidence with clinical expertise.
5. How can healthcare institutions support EBP?
- Healthcare institutions can support EBP by providing access to resources, offering training and education, and fostering a culture of evidence-based decision-making.





